The sheds
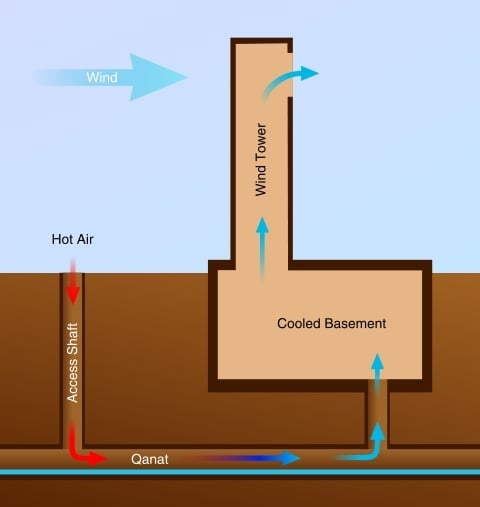
The sheds are towers connected to the buildings used for cooling, used in mosques and hospitals on a large scale, during the Abbasid period all hospitals were equipped with airways and most of the houses. The tower has air ports above the building's facades to pull cold air from the bottom to enter the interior of the house. Because the movement of the outside air passing through the top of the tower creates a pressure difference that helps to pull the hot air from the inside, so the combination of the hooks with the Mashrabiya - open on the inner courtyard - ensures a constant renewal of the air of the rooms. Different types of air intake, where their forms and functions are based on surrounding climatic conditions, the most common are unidirectional and multi-directional air intake.
Characteristics of the picker:
1 provides natural ventilation, by taking clean air free of dust and impurities from the upper layers of outer space, and making it flow through the interior spaces, and helps to increase the speed of air inside the building.
2 helps to reduce the noise coming from the outside, which accompany the ventilation through the window.
Types of attachments: Types of attachments:
Unidirectional air intake: A high-rise tower with wind-driven air outlets. Where the cold air picks up and passes it to the interior spaces of the building. The size of the outlet is determined by the temperature of the external air; if the temperature is high, the smaller size is required, but if it is low, it is better to be large.
Multi-directional air intake: A four-way latch that absorbs air from any direction. The air coming from this outlet can be moistened and cooled by placing a porous ceramic pot full of water. The square shape is the most common.
Air Tracks: Used to pull hot air out of the cabins into the outside air that replaces the wet air coming from the yard. It shows the opposite direction of prevailing winds.
Wall air intake: depends on the idea of the impact of wind pressure on the large surfaces of the walls of the rooms, appear from the outside in the form of hollow horizontal hooks, located in the middle of the height of the outer wall and the bottom of the alcove has a shutter to control the opening or closing from the inside. The high-pressure air passing through the outer wall of the room facing the wind gathers inside the loops and pushes inside through the openings, causing air movement inside.